Germany’s top prosecutor files motion for asset forfeiture of $789 million of frozen Russian money
Mainstream China funds, on average, put over half of their assets under management into just 1% of stocks. The remaining 98%–99% of the China stock universe is arguably underexplored. We believe there are favorable excess return opportunities beyond the well‑discovered large-cap consensus names. In many traditional industries, we’ve seen better capital expenditure (capex) discipline and industry consolidation. This may still be true for some emerging industries, but in more mature sectors, things have changed.
If you earn more than £10,000 in interest, you are obliged to complete a self-assessment form. The personal savings allowance means that basic-rate taxpayers can earn up to £1,000 in interest tax-free, while high-rate taxpayers can earn £500. When the best savings rates were only paying about 0.5%, you would have needed £200,000 in savings to breach the allowance. Today, with rates at more than 5%, interest on savings of £20,000 could top the £1,000 allowance. Fixed-rate bonds tie up your money for a set amount of time and offer a guaranteed rate of interest.
Accounting Topics
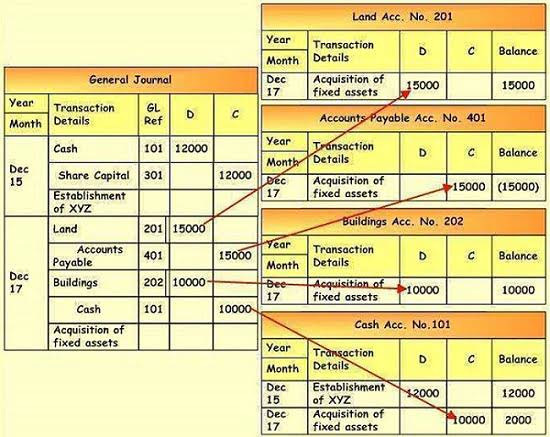
This is posted to the Cash T-account on the debit side (left side). This is posted to the Common Stock T-account on the credit side (right side). Common Stock had a credit of $20,000 in the journal entry, and that information is transferred to the general ledger account in the credit column. The balance at that time in the Common Stock ledger account is $20,000.
The credit is the larger of the two sides ($4,000 on the credit side as opposed to $2,500 on the debit side), so the Accounts Payable account has a credit balance of $1,500. T Accounts are also used for income statement accounts as well, which include revenues, expenses, gains, and losses. They work with the double-entry accounting system to reduce the chance of errors. They are a visual way of recording all transactions that a company makes.
Module 12: Money and Banking
The Federal Reserve requires that banks keep a certain percentage of depositors’ money on “reserve,” which means either in the banks’ own vaults or as deposits kept at the Federal Reserve Bank. T-accounts can also impact balance sheet accounts such as assets as well as income statement accounts such as expenses. T-accounts are used as an aid for managing debits and credits when using double-entry accounting.
- In other words, assets are items that a company uses to generate future revenues or maintain its operations.
- Here, you agree to give a set period of notice before accessing your money.
- T accounts are one of the primary forms of performing double-entry accounting.
- The accounts on the chart of accounts go in the order of the items on the balance sheet and income statement.
- We will use the Cash ledger account to calculate account balances.
- Debits to revenue and gain can reduce the account balance, while credits increase it.
- T Accounts allows businesses that use double entry to distinguish easily between those debits and credits.
A current asset is one that has a useful life of one year or less. Non-current assets have a useful life of longer than one year. A double entry system is time-consuming for a company to implement and maintain, and may require additional manpower for data entry (meaning, more money spent on staff). T Accounts always follow the same structure to record entries – with “debits” on the left, and “credits” on the right.
When Cash Is Debited and Credited
A double-entry accounting system means that every transaction that a company makes is recorded in at least two accounts, where one account gets a “debit” entry while another account gets a “credit” entry. Well organized T accounts are the first step in the bookkeeping and accounting process. If they are inaccurate or hard to follow, then everything from drafting financial statements to forecasting future revenue growth is in jeopardy.
Amortization vs. depreciation: What are the differences? – Thomson Reuters Tax & Accounting
Amortization vs. depreciation: What are the differences?.
Posted: Thu, 07 Dec 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
You will notice that the transactions from January 3, January 9, and January 12 are listed already in this T-account. The next transaction figure of $100 is added directly below the January 12 record on the credit side. Another way to visualize business transactions is to write a general journal entry. Each general journal entry lists the date, the account title(s) to be debited and the corresponding amount(s) followed by the account title(s) to be credited and the corresponding amount(s). Let’s illustrate the general journal entries for the two transactions that were shown in the T-accounts above. Savings banks and life insurance companies do not suffer large net outflows very often.
The two totals for each must balance, otherwise there is an error in the recording. If a bank makes most of its loans in a local area, then the bank may be financially vulnerable if the local economy declines, so that many people are unable to make their payments. But if a bank sells its local loans, t accounts and then buys a mortgage-backed security based on home loans in many parts of the country, it can avoid being exposed to local financial risks. T-accounts can be a useful resource for bookkeeping and accounting novices, helping them understand debits, credits, and double-entry accounting principles.

Once again, debits to revenue/gain decrease the account while credits increase the account. Putting all the accounts together, we can examine the following. In this case, you debit $20,000 in the cash T account and credit $20,000 in the revenue T account. Two entries (hence, double entry), one on the left and one on the right, so everything is good. Two asset accounts, Allowance for Doubtful Accounts and Accumulated Depreciation, are known as contra asset accounts since these accounts are expected to have credit balances. A T-Account is an accounting tool used to track debits and credits for a single account.

